本文主要聚焦于 App 端的 Insets(不是 WMS 端),从以下几个问题入手 Insets 相关的源码。
- 什么是 Insets ?
- Insets 来自哪里
- Insets 如何分发给 View
1. 什么是 Insets ?
Insets 在中文语境中,没有一个特别准确的对应词,Google 的文档以及博客将其翻译为边衬区。
Insets 描述的是显示屏幕上的一些矩形区域,这些区域是系统 UI 所在的区域,常见的有 StatusBar NavigationBar IME(输入法)等
既然是系统 UI,那为什么 App 端还需要去关注 Insets 呢?Activity 如果进行了显示方面的配置,Activity 的显示区域可能就会和 Insets 重叠。
比如我们配置了全屏的主题:
android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Black.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen"
或者配置了 window 的全屏 flag:
requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
那么 Activity 就会从 statusbar 下面开始布局和绘制:
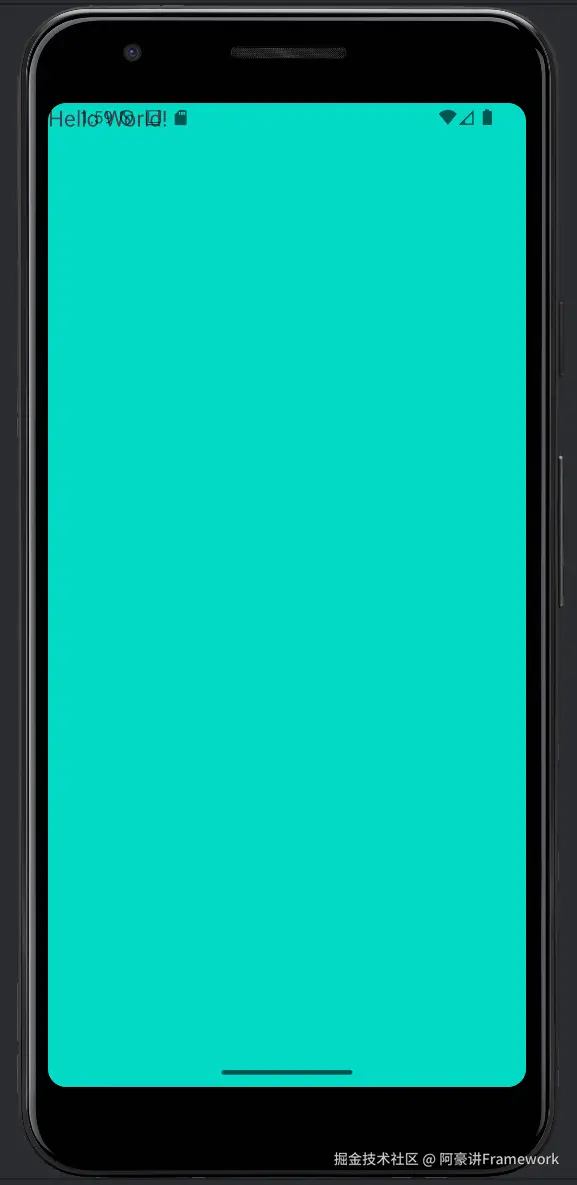
要处理这种 App 界面与系统 UI 界面重叠的情况都需要了解 Insets。
最常见的场景就是沉浸式状态栏,沉浸式状态栏应该是每个 Android App 开发都处理过的恶心需求,不同的系统版本,不同的手机品牌(小米,魅族)都需要单独的适配!!!
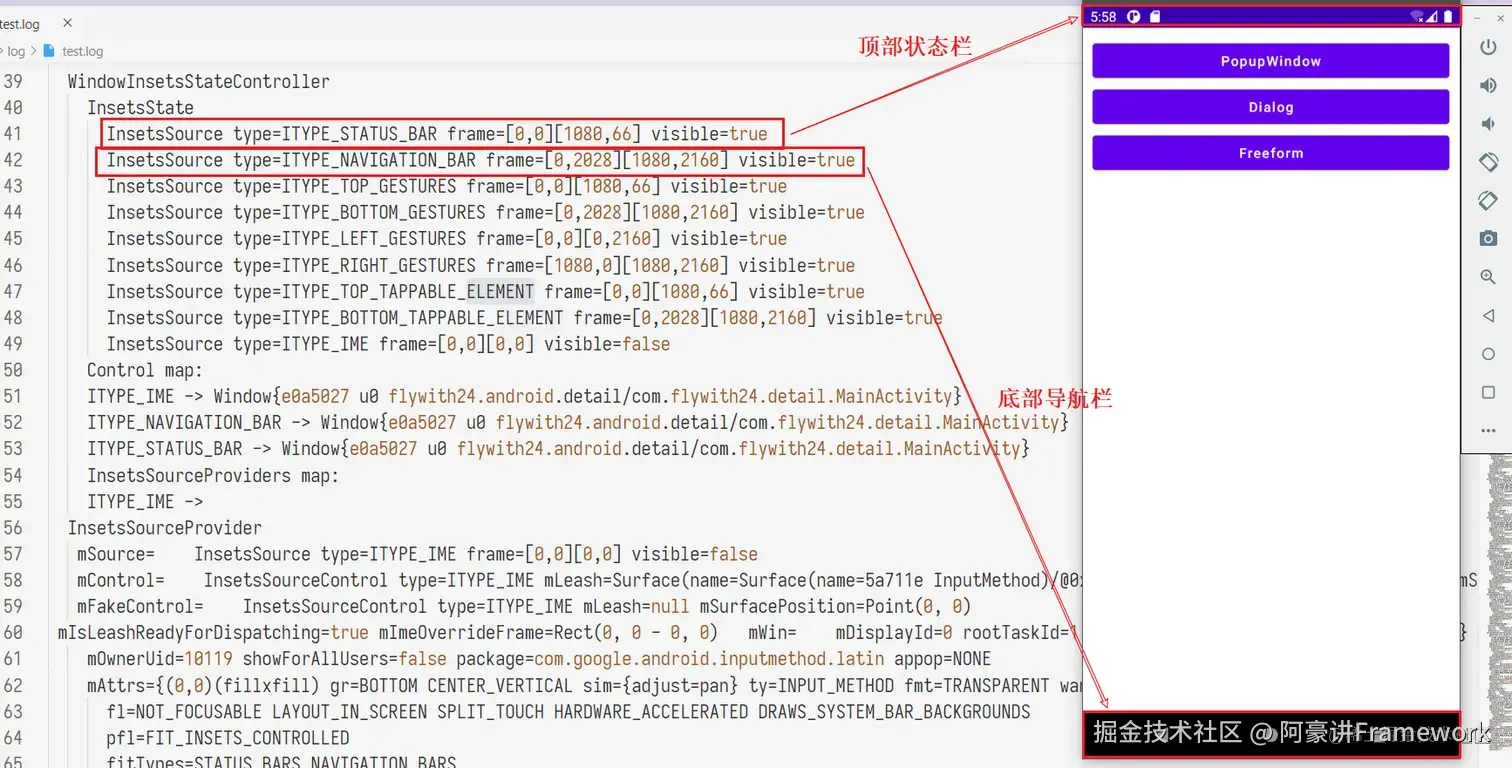
我们可以通过 adb shell dumpsys activity 命令可以查看到 Insets 相关的信息:
那么源码中如何表示/描述一个 Insets,在 App 端使用 Insets 类:
public final class Insets implements Parcelable {
public static final @NonNull Insets NONE = new Insets(0, 0, 0, 0);
public final int left;
public final int top;
public final int right;
public final int bottom;
private Insets(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
}
举个 Insets 对象的实际例子:
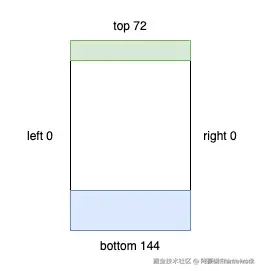
这里的 left top right bottom,描述的是一个偏移量,图片中有颜色的区域就是 insets 所在区域。
Insets 有很多类型,比如:
- StatusBar
- NavigationBar
- 系统手势区
- 刘海区
- 输入法
- …….
WindowInsets.Type 类中定义了多个常量来表示 Insets 的类型:
public final class WindowInsets {
public static final class Type {
static final int FIRST = 1;
static final int STATUS_BARS = FIRST;
static final int NAVIGATION_BARS = 1 << 1;
static final int CAPTION_BAR = 1 << 2;
static final int IME = 1 << 3;
static final int SYSTEM_GESTURES = 1 << 4;
static final int MANDATORY_SYSTEM_GESTURES = 1 << 5;
static final int TAPPABLE_ELEMENT = 1 << 6;
static final int DISPLAY_CUTOUT = 1 << 7;
static final int LAST = 1 << 8;
static final int SIZE = 9;
static final int WINDOW_DECOR = LAST;
private Type() {}
}
}
具体每个类型的 Inset 的介绍可以查看官方博客处理视觉冲突 | 手势导航 (二)
2. Insets 来自哪里
2.1 App 中如何获取到 Insets
首先从 App 开发的角度,我们可以通过 View 的 setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener 方法设置一个回调对象来获取到 Insets:
val main:View = findViewById(R.id.main)
main.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener { v, insets ->
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
Log.d("zzh","top is ${systemBars.top}")
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom)
insets
}
如果是通用 App,推荐使用 AndroidX 提供的兼容库来实现:
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main)) { v, insets ->
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom)
Log.d("zzh","top is ${systemBars.top}")
insets
}
setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener 中返回的数据的类型是 WindowInsets。
WindowInset 中有一个成员 private final Insets[] mTypeInsetsMap; 该成员保存了所有的 Insets。
public final class WindowInsets {
private final Insets[] mTypeInsetsMap;
public Insets getInsets(@InsetsType int typeMask) {
return getInsets(mTypeInsetsMap, typeMask);
}
static Insets getInsets(Insets[] typeInsetsMap, @InsetsType int typeMask) {
Insets result = null;
for (int i = FIRST; i <= LAST; i = i << 1) {
if ((typeMask & i) == 0) {
continue;
}
Insets insets = typeInsetsMap[indexOf(i)];
if (insets == null) {
continue;
}
if (result == null) {
result = insets;
} else {
result = Insets.max(result, insets);
}
}
return result == null ? Insets.NONE : result;
}
}
我们只需要传入一个 WindowInsets.Type 类型,就可以通过 WindowInsets::getInsets 方法获取到具体类型的 Insets 对象。
2.2 获取 InsetsState
那么这里的 Inset 是从哪里来的呢?
在 Activity/Window 的显示过程中,相关的调用链如下:
ViewRootImpl::setView
ViewRootImpl::requestLayout
ViewRootImpl::scheduleTraversals
ViewRootImpl.TraversalRunnable::run -- 异步操作
ViewRootImpl::doTraversal
ViewRootImpl::performTraversals
ViewRootImpl::dispatchApplyInsets -- 第二步,计算并分发 Insets
ViewRootImpl::relayoutWindow
mWindowSession::relayout -- 第三步,获取 InsetsSourceControl
InsetsController::onControlsChanged -- 分发 InsetsSourceControl
Session.addToDisplayAsUser -- 第一步,获取 InsetsState
InsetsController::onStateChanged -- 分发 InsetsState
在 addToDisplayAsUser 的时候,会从 wms 中获取到 private final InsetsState mTempInsets
private final InsetsState mTempInsets = new InsetsState();
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId,
mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibleTypes(), inputChannel, mTempInsets,
mTempControls, attachedFrame, compatScale);
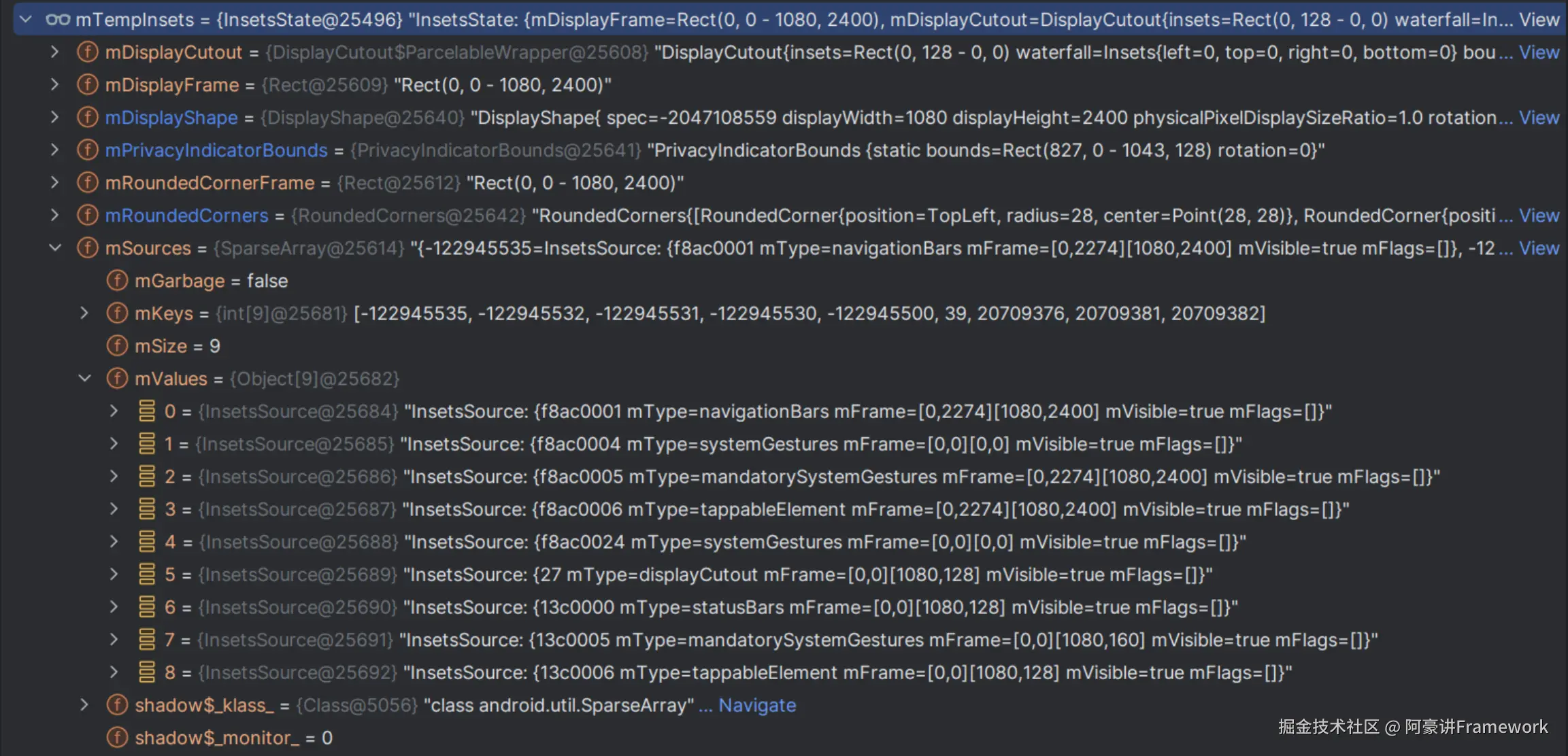
InsetsState 又是什么?
InsetsState 保存了系统中所有的 Insets 的状态/信息
public class InsetsState implements Parcelable {
private final SparseArray mSources;
WindowInsets calculateInsets(...) {
}
}
InsetsState 内部成员 private final SparseArray 对应了每一个 Insets。
从 adb shell dumpsys activity 打印的信息可以看出对应关系:
InsetsSource id=f8ac0001 type=navigationBars frame=[0,2274][1080,2400] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=f8ac0004 type=systemGestures frame=[0,0][0,0] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=f8ac0005 type=mandatorySystemGestures frame=[0,2274][1080,2400] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=f8ac0006 type=tappableElement frame=[0,2274][1080,2400] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=f8ac0024 type=systemGestures frame=[0,0][0,0] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=3 type=ime frame=[0,0][0,0] visible=false flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=27 type=displayCutout frame=[0,0][1080,128] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=13c0000 type=statusBars frame=[0,0][1080,128] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=13c0005 type=mandatorySystemGestures frame=[0,0][1080,160] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource id=13c0006 type=tappableElement frame=[0,0][1080,128] visible=true flags= insetsRoundedCornerFrame=false
InsetsSource 的实现如下:
public class InsetsSource implements Parcelable {
private final @InternalInsetsType int mType;
private final Rect mFrame;
private boolean mVisible;
}
InsetsState 中还有一个重要的方法 calculateInsets,该方法基于 mSources 计算出 windowInsets。这里没有具体的情景,源码我们先不分析。
2.3 获取 InsetsSourceControl
App 在 relayout 的时候,会从 wms 中获取到 InsetsSourceControl.Array mTempControls
private final InsetsSourceControl.Array mTempControls = new InsetsSourceControl.Array();
relayoutResult = mWindowSession.relayout(mWindow, params,
requestedWidth, requestedHeight, viewVisibility,
insetsPending ? WindowManagerGlobal.RELAYOUT_INSETS_PENDING : 0, mRelayoutSeq,
mLastSyncSeqId, mTmpFrames, mPendingMergedConfiguration, mSurfaceControl,
mTempInsets, mTempControls, mRelayoutBundle);
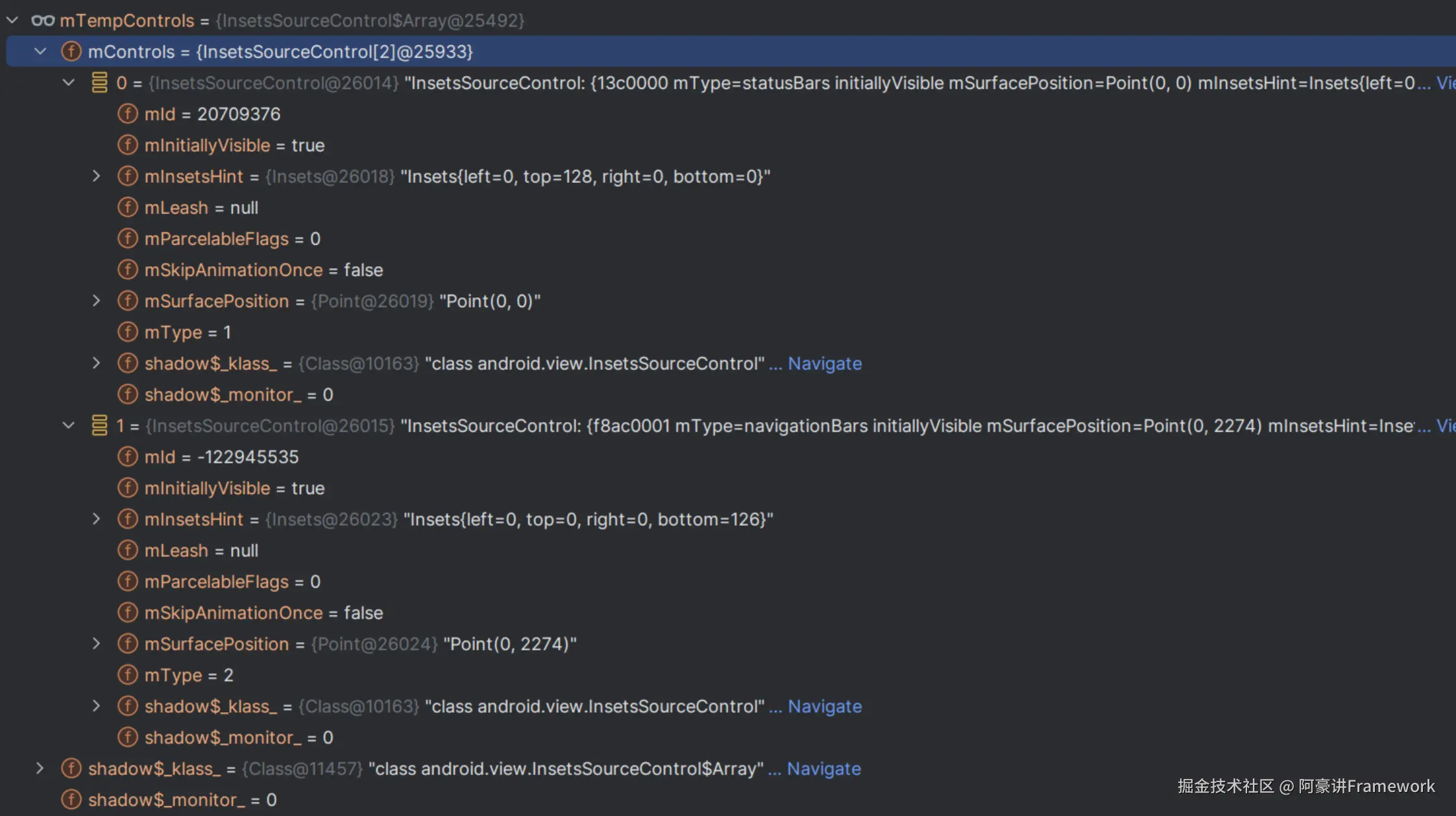
public static class Array implements Parcelable {
private @Nullable InsetsSourceControl[] mControls;
}
可以看出 InsetsSourceControl.Array 实际就是 InsetsSourceControl 的数组。
InsetsSourceControl 对象与一个具体的 Insets 对应,主要用于控制 Insets 的显示与隐藏,输入法会涉及的场景会比较多一些。
public class InsetsSourceControl implements Parcelable {
private final int mId;
private final @InsetsType int mType;
private final Point mSurfacePosition;
private Insets mInsetsHint;
}
通过 adb shell dumpsys activity 命令可以查看到 InsetsSourceControl 相关的信息:
InsetsSourceControl: {13c0000 mType=statusBars initiallyVisible mSurfacePosition=Point(0, 0) mInsetsHint=Insets{left=0, top=128, right=0, bottom=0}}
InsetsSourceControl: {f8ac0001 mType=navigationBars initiallyVisible mSurfacePosition=Point(0, 2274) mInsetsHint=Insets{left=0, top=0, right=0, bottom=126}}
InsetsSourceControl: {3 mType=ime mSurfacePosition=Point(0, 128) mInsetsHint=Insets{left=0, top=0, right=0, bottom=0}}
3. Insets 相关数据的分发
3.1 InsetsState 的分发
在调用 Session.addToDisplayAsUser 获取到 InsetsState 后,会调用到 InsetsController::onStateChanged 方法。
这里使用到了 InsetsController,它又是干什么的?
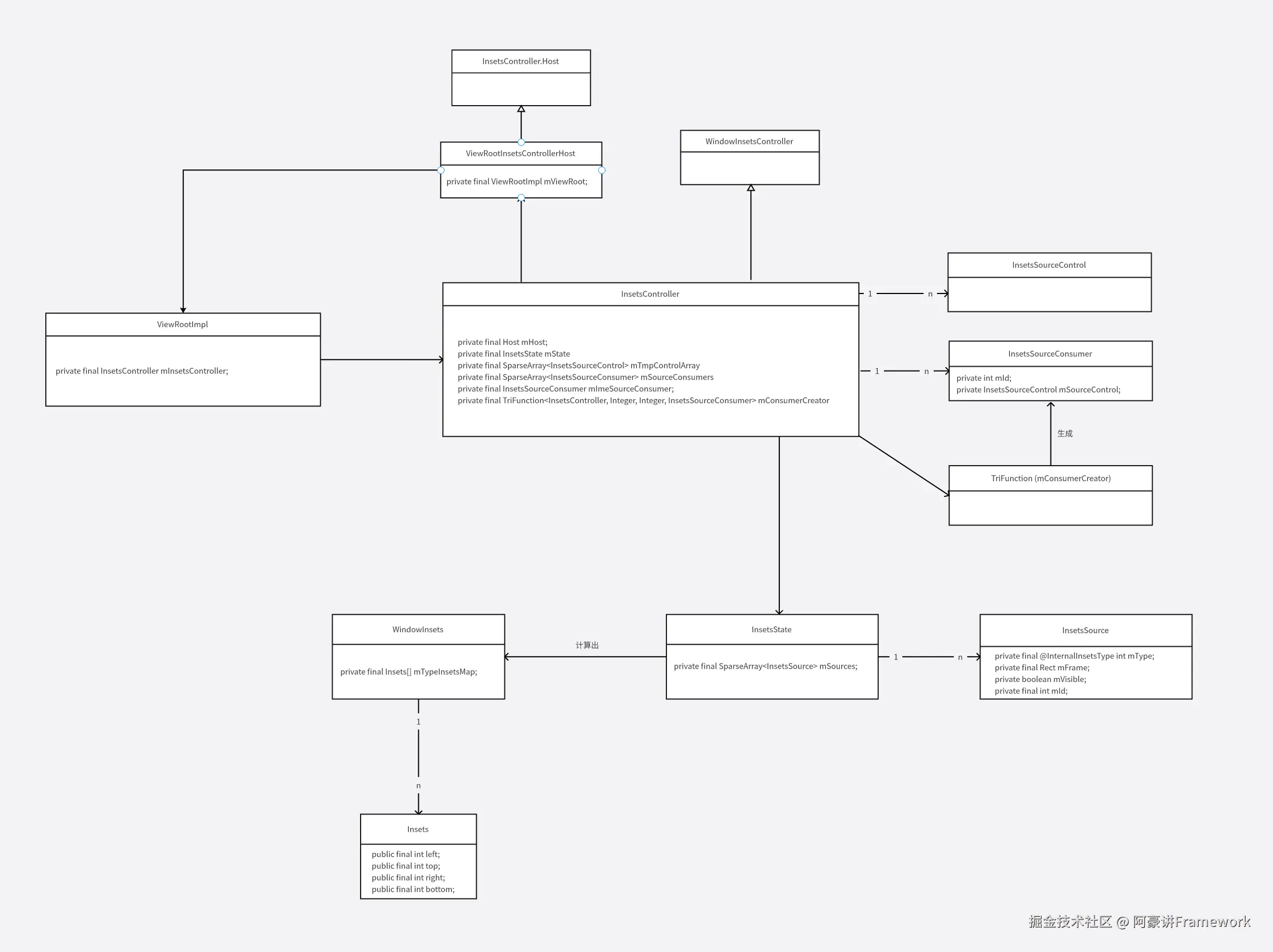
每个 窗口/ViewRootImpl 对应一个 InsetController,用于控制 insets 的显示,隐藏,状态更新以及动画的调度。
InsetsController 在 ViewRootImpl 初始化时构建并初始化。
private final InsetsController mInsetsController;
public ViewRootImpl(@UiContext Context context, Display display, IWindowSession session,
WindowLayout windowLayout) {
mInsetsController = new InsetsController(new ViewRootInsetsControllerHost(this));
}
InsetsController 的实现如下:
public class InsetsController implements WindowInsetsController, InsetsAnimationControlCallbacks {
private final Host mHost;
private final InsetsState mState = new InsetsState();
private final SparseArray mTmpControlArray = new SparseArray<>();
private final TriFunction mConsumerCreator;
private final SparseArray mSourceConsumers = new SparseArray<>();
private final InsetsSourceConsumer mImeSourceConsumer;
public InsetsController(Host host) {
this(host, (controller, id, type) -> {
if (type == ime()) {
return new ImeInsetsSourceConsumer(id, controller.mState,
Transaction::new, controller);
} else {
return new InsetsSourceConsumer(id, type, controller.mState,
Transaction::new, controller);
}
}, host.getHandler());
}
@VisibleForTesting
public InsetsController(Host host,
TriFunction consumerCreator,
Handler handler) {
mHost = host;
mConsumerCreator = consumerCreator;
mHandler = handler;
mAnimCallback = () -> {
};
mImeSourceConsumer = getSourceConsumer(ID_IME, ime());
}
@VisibleForTesting
public @NonNull InsetsSourceConsumer getSourceConsumer(int id, int type) {
InsetsSourceConsumer consumer = mSourceConsumers.get(id);
if (consumer != null) {
return consumer;
}
if (type == ime() && mImeSourceConsumer != null) {
mSourceConsumers.remove(mImeSourceConsumer.getId());
consumer = mImeSourceConsumer;
consumer.setId(id);
} else {
consumer = mConsumerCreator.apply(this, id, type);
}
mSourceConsumers.put(id, consumer);
return consumer;
}
}
InsetsController 有一个重要成员 SparseArray,是 InsetsSource 的消费者。
InsetsController 的另一个成员 InsetsSourceConsumer mImeSourceConsumer;(InsetsSourceConsumer 的子类) 是 Ime InsetSource 的消费者。
InsetsSourceConsumer 中有几个重要的方法:
public void updateSource(InsetsSource newSource, @AnimationType int animationType)
public int requestShow(boolean fromController, @Nullable ImeTracker.Token statsToken)
void requestHide(boolean fromController, @Nullable ImeTracker.Token statsToken)
这里消费的意思是什么? 应该是指执行 Insets 的 show or hide 操作。
InsetsController 的另外一个成员 mConsumerCreator 用于生成 InsetsSourceConsumer。mConsumerCreator 在构造函数中初始化。
接下来就来看 onStateChanged 方法的实现:
@VisibleForTesting
public boolean onStateChanged(InsetsState state) {
boolean stateChanged = false;
if (!CAPTION_ON_SHELL) {
stateChanged = !mState.equals(state, true ,
false )
|| captionInsetsUnchanged();
} else {
stateChanged = !mState.equals(state, false ,
false );
}
if (!stateChanged && mLastDispatchedState.equals(state)) {
return false;
}
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onStateChanged: " + state);
mLastDispatchedState.set(state, true );
final InsetsState lastState = new InsetsState(mState, true );
updateState(state);
applyLocalVisibilityOverride();
updateCompatSysUiVisibility();
if (!mState.equals(lastState, false ,
true )) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onStateChanged, notifyInsetsChanged");
mHost.notifyInsetsChanged();
if (lastState.getDisplayFrame().equals(mState.getDisplayFrame())) {
InsetsState.traverse(lastState, mState, mStartResizingAnimationIfNeeded);
}
}
return true;
}
这里我们主要关心 updateState 方法,该方法会把从 WMS 中获取到的 InsetState 保存到 InsetsController 的成员 private final InsetsState mState 中。
3.2 dispatchApplyInsets 计算和分发 Insets
接下来会调用到 dispatchApplyInsets 方法,从名字就可以看出来,该方法用于分发 Insets:
public void dispatchApplyInsets(View host) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "dispatchApplyInsets");
mApplyInsetsRequested = false;
WindowInsets insets = getWindowInsets(true );
if (!shouldDispatchCutout()) {
insets = insets.consumeDisplayCutout();
}
host.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
mAttachInfo.delayNotifyContentCaptureInsetsEvent(insets.getInsets(Type.all()));
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
这里主要两个关键点:
- getWindowInsets,计算 Insets,实际就是将从 WMS 获取到的 InsetsState 转换为 App 需要的 InsetState
- dispatchApplyWindowInsets,将 WindowInsets 分发给 View
3.2.1 getWindowInsets 计算 Insets
getWindowInsets 的实现如下:
private WindowInsets mLastWindowInsets;
WindowInsets getWindowInsets(boolean forceConstruct) {
if (mLastWindowInsets == null || forceConstruct) {
final Configuration config = getConfiguration();
mLastWindowInsets = mInsetsController.calculateInsets(
config.isScreenRound(), mAttachInfo.mAlwaysConsumeSystemBars,
mWindowAttributes.type, config.windowConfiguration.getWindowingMode(),
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode, mWindowAttributes.flags,
(mWindowAttributes.systemUiVisibility
| mWindowAttributes.subtreeSystemUiVisibility));
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets.set(mLastWindowInsets.getSystemWindowInsets().toRect());
mAttachInfo.mStableInsets.set(mLastWindowInsets.getStableInsets().toRect());
mAttachInfo.mVisibleInsets.set(mInsetsController.calculateVisibleInsets(
mWindowAttributes.type, config.windowConfiguration.getWindowingMode(),
mWindowAttributes.softInputMode, mWindowAttributes.flags).toRect());
}
return mLastWindowInsets;
}
接着调用 InsetsController::calculateInsets 计算 Insets:
private WindowInsets mLastInsets;
private final InsetsState mState = new InsetsState();
@VisibleForTesting
public WindowInsets calculateInsets(boolean isScreenRound, boolean alwaysConsumeSystemBars,
int windowType, int windowingMode, int legacySoftInputMode, int legacyWindowFlags,
int legacySystemUiFlags) {
mWindowType = windowType;
mLastWindowingMode = windowingMode;
mLastLegacySoftInputMode = legacySoftInputMode;
mLastLegacyWindowFlags = legacyWindowFlags;
mLastLegacySystemUiFlags = legacySystemUiFlags;
mLastInsets = mState.calculateInsets(mFrame, null ,
isScreenRound, alwaysConsumeSystemBars, legacySoftInputMode, legacyWindowFlags,
legacySystemUiFlags, windowType, windowingMode, null );
return mLastInsets;
}
接着调用 InsetsState::calculateInsets:
private final SparseArray mSources;
public WindowInsets calculateInsets(Rect frame, @Nullable InsetsState ignoringVisibilityState,
boolean isScreenRound, boolean alwaysConsumeSystemBars,
int legacySoftInputMode, int legacyWindowFlags, int legacySystemUiFlags,
int windowType, @WindowConfiguration.WindowingMode int windowingMode,
@Nullable @InternalInsetsSide SparseIntArray idSideMap) {
Insets[] typeInsetsMap = new Insets[Type.SIZE];
Insets[] typeMaxInsetsMap = new Insets[Type.SIZE];
boolean[] typeVisibilityMap = new boolean[Type.SIZE];
final Rect relativeFrame = new Rect(frame);
final Rect relativeFrameMax = new Rect(frame);
@InsetsType int suppressScrimTypes = 0;
for (int i = mSources.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final InsetsSource source = mSources.valueAt(i);
if ((source.getFlags() & InsetsSource.FLAG_SUPPRESS_SCRIM) != 0) {
suppressScrimTypes |= source.getType();
}
processSource(source, relativeFrame, false , typeInsetsMap,
idSideMap, typeVisibilityMap);
if (source.getType() != WindowInsets.Type.ime()) {
InsetsSource ignoringVisibilitySource = ignoringVisibilityState != null
? ignoringVisibilityState.peekSource(source.getId())
: source;
if (ignoringVisibilitySource == null) {
continue;
}
processSource(ignoringVisibilitySource, relativeFrameMax,
true , typeMaxInsetsMap, null ,
null );
}
}
final int softInputAdjustMode = legacySoftInputMode & SOFT_INPUT_MASK_ADJUST;
@InsetsType int compatInsetsTypes = systemBars() | displayCutout();
if (softInputAdjustMode == SOFT_INPUT_ADJUST_RESIZE) {
compatInsetsTypes |= ime();
}
if ((legacyWindowFlags & FLAG_FULLSCREEN) != 0) {
compatInsetsTypes &= ~statusBars();
}
if (clearsCompatInsets(windowType, legacyWindowFlags, windowingMode)
&& !alwaysConsumeSystemBars) {
compatInsetsTypes = 0;
}
return new WindowInsets(typeInsetsMap, typeMaxInsetsMap, typeVisibilityMap, isScreenRound,
alwaysConsumeSystemBars, suppressScrimTypes, calculateRelativeCutout(frame),
calculateRelativeRoundedCorners(frame),
calculateRelativePrivacyIndicatorBounds(frame),
calculateRelativeDisplayShape(frame),
compatInsetsTypes, (legacySystemUiFlags & SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LAYOUT_STABLE) != 0);
}
接着看
private void processSource(InsetsSource source, Rect relativeFrame, boolean ignoreVisibility,
Insets[] typeInsetsMap, @Nullable @InternalInsetsSide SparseIntArray idSideMap,
@Nullable boolean[] typeVisibilityMap) {
Insets insets = source.calculateInsets(relativeFrame, ignoreVisibility);
final int type = source.getType();
processSourceAsPublicType(source, typeInsetsMap, idSideMap, typeVisibilityMap,
insets, type);
if (type == Type.MANDATORY_SYSTEM_GESTURES) {
processSourceAsPublicType(source, typeInsetsMap, idSideMap, typeVisibilityMap,
insets, Type.SYSTEM_GESTURES);
}
if (type == Type.CAPTION_BAR) {
processSourceAsPublicType(source, typeInsetsMap, idSideMap, typeVisibilityMap,
insets, Type.SYSTEM_GESTURES);
processSourceAsPublicType(source, typeInsetsMap, idSideMap, typeVisibilityMap,
insets, Type.MANDATORY_SYSTEM_GESTURES);
processSourceAsPublicType(source, typeInsetsMap, idSideMap, typeVisibilityMap,
insets, Type.TAPPABLE_ELEMENT);
}
}
接着调用 calculateInsets 方法
private Insets calculateInsets(Rect relativeFrame, Rect frame, boolean ignoreVisibility) {
if (!ignoreVisibility && !mVisible) {
return Insets.NONE;
}
if (getType() == WindowInsets.Type.captionBar()) {
return Insets.of(0, frame.height(), 0, 0);
}
final boolean hasIntersection = relativeFrame.isEmpty()
? getIntersection(frame, relativeFrame, mTmpFrame)
: mTmpFrame.setIntersect(frame, relativeFrame);
if (!hasIntersection) {
return Insets.NONE;
}
if (getType() == WindowInsets.Type.ime()) {
return Insets.of(0, 0, 0, mTmpFrame.height());
}
if (mTmpFrame.width() == relativeFrame.width()) {
if (mTmpFrame.top == relativeFrame.top) {
return Insets.of(0, mTmpFrame.height(), 0, 0);
} else if (mTmpFrame.bottom == relativeFrame.bottom) {
return Insets.of(0, 0, 0, mTmpFrame.height());
}
if (mTmpFrame.top == 0) {
return Insets.of(0, mTmpFrame.height(), 0, 0);
}
}
else if (mTmpFrame.height() == relativeFrame.height()) {
if (mTmpFrame.left == relativeFrame.left) {
return Insets.of(mTmpFrame.width(), 0, 0, 0);
} else if (mTmpFrame.right == relativeFrame.right) {
return Insets.of(0, 0, mTmpFrame.width(), 0);
}
}
return Insets.NONE;
}
不同的条件生成不同的 Insets 返回。
processSourceAsPublicType 将生成的 Insets 插入会数组中。
private void processSourceAsPublicType(InsetsSource source, Insets[] typeInsetsMap,
@InternalInsetsSide @Nullable SparseIntArray idSideMap,
@Nullable boolean[] typeVisibilityMap, Insets insets, int type) {
int index = indexOf(type);
Insets existing = typeInsetsMap[index];
if (existing == null) {
typeInsetsMap[index] = insets;
} else {
typeInsetsMap[index] = Insets.max(existing, insets);
}
if (typeVisibilityMap != null) {
typeVisibilityMap[index] = source.isVisible();
}
if (idSideMap != null) {
@InternalInsetsSide int insetSide = getInsetSide(insets);
if (insetSide != ISIDE_UNKNOWN) {
idSideMap.put(source.getId(), insetSide);
}
}
}
3.2.2 dispatchApplyWindowInsets 分发 Insets
我们接着看 dispatchApplyWindowInsets 分发 Insets 的过程:
@Override
public WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
insets = super.dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
if (insets.isConsumed()) {
return insets;
}
if (View.sBrokenInsetsDispatch) {
return brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
} else {
return newDispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
}
无论那种情况都会去调用 View::dispatchApplyWindowInsets
private WindowInsets brokenDispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
insets = getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
if (insets.isConsumed()) {
break;
}
}
return insets;
}
private WindowInsets newDispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
getChildAt(i).dispatchApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
return insets;
}
View::dispatchApplyWindowInsets 的实现如下:
public WindowInsets dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets) {
try {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS;
if (mListenerInfo != null && mListenerInfo.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener != null) {
return mListenerInfo.mOnApplyWindowInsetsListener.onApplyWindowInsets(this, insets);
} else {
return onApplyWindowInsets(insets);
}
} finally {
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_APPLYING_INSETS;
}
}
优先调用 Listener,其次调用覆写方法,二选一,不会被同时调用。
3.3 InsetsSourceControl 的分发
我们接着看 onControlsChanged 分发 InsetsSourceControl 的过程:
private final SparseArray mTmpControlArray = new SparseArray<>();
private final SparseArray mSourceConsumers = new SparseArray<>();
public void onControlsChanged(InsetsSourceControl[] activeControls) {
if (activeControls != null) {
for (InsetsSourceControl activeControl : activeControls) {
if (activeControl != null) {
mTmpControlArray.put(activeControl.getId(), activeControl);
}
}
}
@InsetsType int controllableTypes = 0;
int consumedControlCount = 0;
final @InsetsType int[] showTypes = new int[1];
final @InsetsType int[] hideTypes = new int[1];
for (int i = mSourceConsumers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final InsetsSourceConsumer consumer = mSourceConsumers.valueAt(i);
final InsetsSourceControl control = mTmpControlArray.get(consumer.getId());
if (control != null) {
controllableTypes |= control.getType();
consumedControlCount++;
}
consumer.setControl(control, showTypes, hideTypes);
}
if (consumedControlCount != mTmpControlArray.size()) {
for (int i = mTmpControlArray.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final InsetsSourceControl control = mTmpControlArray.valueAt(i);
getSourceConsumer(control.getId(), control.getType())
.setControl(control, showTypes, hideTypes);
}
}
if (mTmpControlArray.size() > 0) {
for (int i = mRunningAnimations.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
mRunningAnimations.get(i).runner.updateSurfacePosition(mTmpControlArray);
}
}
mTmpControlArray.clear();
int animatingTypes = invokeControllableInsetsChangedListeners();
showTypes[0] &= ~animatingTypes;
hideTypes[0] &= ~animatingTypes;
if (showTypes[0] != 0) {
applyAnimation(showTypes[0], true , false ,
null );
}
if (hideTypes[0] != 0) {
applyAnimation(hideTypes[0], false , false ,
null );
}
if (mControllableTypes != controllableTypes) {
if (WindowInsets.Type.hasCompatSystemBars(mControllableTypes ^ controllableTypes)) {
mCompatSysUiVisibilityStaled = true;
}
mControllableTypes = controllableTypes;
}
reportRequestedVisibleTypes();
}
}
核心两点:
- 把 Control 保存到 mTmpControlArray 中
- 把 consumer 和 control 关联起来,他两一起负责 Insets 的显示与隐藏
最后给出一个相关类的类图:
参考资料
1、本站所有资源均从互联网上收集整理而来,仅供学习交流之用,因此不包含技术服务请大家谅解!
2、本站不提供任何实质性的付费和支付资源,所有需要积分下载的资源均为网站运营赞助费用或者线下劳务费用!
3、本站所有资源仅用于学习及研究使用,您必须在下载后的24小时内删除所下载资源,切勿用于商业用途,否则由此引发的法律纠纷及连带责任本站和发布者概不承担!
4、本站站内提供的所有可下载资源,本站保证未做任何负面改动(不包含修复bug和完善功能等正面优化或二次开发),但本站不保证资源的准确性、安全性和完整性,用户下载后自行斟酌,我们以交流学习为目的,并不是所有的源码都100%无错或无bug!如有链接无法下载、失效或广告,请联系客服处理!
5、本站资源除标明原创外均来自网络整理,版权归原作者或本站特约原创作者所有,如侵犯到您的合法权益,请立即告知本站,本站将及时予与删除并致以最深的歉意!
6、如果您也有好的资源或教程,您可以投稿发布,成功分享后有站币奖励和额外收入!
7、如果您喜欢该资源,请支持官方正版资源,以得到更好的正版服务!
8、请您认真阅读上述内容,注册本站用户或下载本站资源即您同意上述内容!
原文链接:https://www.dandroid.cn/archives/22019,转载请注明出处。


评论0